Fatal Error: Maximum Execution Time Exceeded in WordPress (7 Safe Fixes)
⚠️ Exact error
Fatal error: Maximum execution time of XX seconds exceeded
🖥️ Platform
WordPress (self-hosted)
🧭 Introduction
Don’t panic. This error looks serious, but it does not mean your site is deleted or permanently broken.
This message appears when WordPress takes longer than PHP allows to complete a task. To prevent server overload, PHP stops execution and shows the Maximum Execution Time Exceeded in WordPress error instead of continuing indefinitely.
The error commonly appears during plugin installs, updates, imports, backups, or migrations. In most cases, your site’s data is still intact — the task simply needs more time or needs to be stopped and corrected.
📌 Quick cause summary
WordPress shows this error when a request runs longer than PHP’s maximum execution time.
This error is different from memory exhaustion.
It occurs because a task takes too long to finish, not because WordPress runs out of memory.
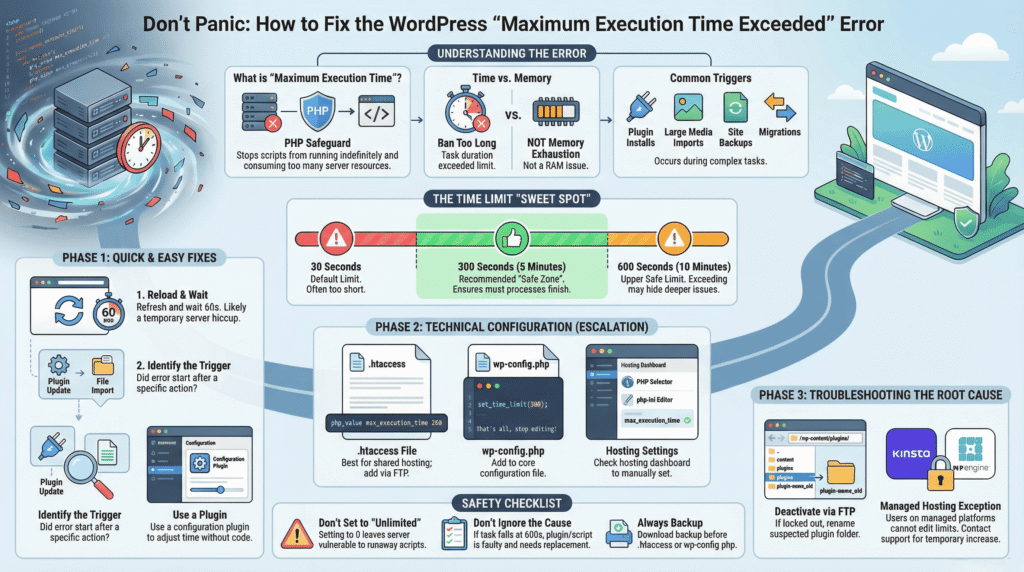
⏱️ Quick reference: execution time limits
- Default PHP limit: 30 seconds
- Recommended for WordPress tasks: 300 seconds (5 minutes)
- Upper safe limit: 600 seconds (10 minutes)
Going higher is not recommended and may hide deeper issues.
❓ Why this happens
When WordPress performs certain actions, PHP must:
- Load WordPress core files
- Load all active plugins
- Load the active theme
- Execute a task (import, update, backup, API request)
Each request has a time limit enforced by the server.
If the task does not finish within that time (often 30 or 60 seconds), PHP stops execution and throws this error.
This safeguard exists to prevent runaway scripts from consuming server resources.
🔧 Step-by-step safe fixes
(Start at Step 1 and stop as soon as the error disappears.)
✅ Step 1: Reload once to confirm it is not temporary
Before changing anything:
- Reload the page once
- Wait 30–60 seconds and try again
If the page loads normally, the issue was caused by a temporary delay.
Risk: None
🔍 Step 2: Identify what action triggered the error
This error almost always appears after a specific action. Think back:
- Did you install or update a plugin?
- Did you import content or media?
- Did you run a backup or migration?
- Did an update stall or freeze?
This context matters.
If the error started immediately after one action, that action is likely the cause.
Risk: None
Method 1: The plugin route (easiest for beginners)
If you prefer not to edit files, you can increase the execution time using a plugin.
Some plugins allow you to adjust execution time safely from the dashboard, such as plugins designed to handle execution time limits or to edit configuration values without touching core files.
This approach is useful if:
- You are not comfortable with FTP or file editing
- You still have access to the WordPress admin area
If the plugin resolves the error, stop here.
Note:
If you are locked out of the dashboard, skip this method and continue to the file-based fixes below.
Risk: Low (no file edits)
Method 2: Increase execution time via .htaccess (most reliable on shared hosting)
On many shared hosting environments (Apache servers), this method is more reliable than wp-config.php.
The .htaccess file controls how the server handles requests for your site.
Adding the execution time here tells the server itself to allow your site more time.
What to do carefully:
- Open your hosting File Manager or connect via FTP
- Navigate to your site’s main directory (commonly
public_html) - Locate the
.htaccessfile - Download a backup copy
- Add this line at the very bottom of the file:
php_value max_execution_time 300- Save the file and reload your site
If the site loads or the task completes, stop here.
If you see a 500 Internal Server Error, remove the line immediately.
This means your host does not allow this method.
Risk: Low (single-line change, fully reversible)
Method 3: Increase execution time via wp-config.php
This method works on some hosts but not all.
Important limitation
On many hosting setups, wp-config.php cannot override server-level execution limits.
If this method does not work, move on to the .htaccess or hosting-level methods.
What to do carefully:
- Open your hosting File Manager or FTP
- Navigate to your site’s main directory
- Locate
wp-config.php - Download a backup copy
- Open the file and find this line:
/* That's all, stop editing! Happy publishing. */- Paste the following code immediately before that line:
set_time_limit(300);- Save the file and reload your site
This allows the current request to run for up to 300 seconds (5 minutes).
It does not make WordPress run indefinitely.
If the site loads, stop here.
Risk: Low (request-level change)
Method 4: Increase execution time via hosting settings or php.ini
Some hosts manage execution limits only at the server level.
Where to look:
- PHP Settings
- Select PHP Version
- PHP Configuration
- php.ini Editor
What to check:
max_execution_timeIf the value is lower than 300:
- Set it to 300
- Save the change
- Reload your site
If your host already allows 300 or more, no change is needed.
Do not guess setting names or create new files unless your host instructs you to.
Risk: Low (host-managed and reversible)
Method 5: Stop the process causing the delay (critical if you are locked out)
If increasing execution time does not resolve the issue, the process itself is likely faulty.
If you cannot access your WordPress dashboard, do this:
- Open File Manager or FTP
- Navigate to:
/wp-content/plugins/- Find the plugin you were installing or updating
- Rename its folder
Example:jetpack→jetpack_old
This forces WordPress to deactivate the plugin.
Reload your site.
If the site loads, that plugin is the cause and should be removed or replaced.
Risk: Low (no data deletion)
🚫 What NOT to do
- Do not set execution time to unlimited
- Do not repeatedly retry failing imports
- Do not reinstall WordPress core files
- Do not ignore the plugin or task causing the delay
⚠️If the issue still persists
If:
- Increasing execution time does not help
- The error appears repeatedly
- The same task always fails
Then the Maximum Execution Time Exceeded in WordPress issue is likely caused by the plugin, theme, or process itself — not the time limit.
For reference on PHP execution limits, see the official PHP documentation.
⛔ Managed hosting users (important)
If you use managed hosting such as Kinsta, WP Engine, or Flywheel, execution time limits are usually locked at the server level.
In this case:
- File edits will not work
- You must contact hosting support and request a temporary execution time increase
This is expected behavior on managed platforms.
📄 Factual summary
The Maximum Execution Time Exceeded in WordPress error occurs when a WordPress task runs longer than PHP allows. In many cases, increasing the execution time to 300 seconds resolves the issue safely.
If the error persists, it usually indicates a slow or faulty plugin, theme, or process — not a WordPress core problem.
Safe troubleshooting starts with confirmation, escalates through controlled configuration changes, and ends by stopping the task that caused the delay.
🔗 Related guides
- Fatal Error: Allowed Memory Size Exhausted in WordPress (How to Fix Safely)
- There Has Been a Critical Error on Your Website in WordPress – What It Means and How to Fix It
- WordPress Stuck in Maintenance Mode After Update – Safe Steps
- How to Fix “Error Establishing a Database Connection” in WordPress (Safely)
❓ FAQ
Is the “Maximum Execution Time Exceeded in WordPress” error related to memory limits?
No. Memory and execution time are separate limits.
Is it safe to increase PHP max execution time in WordPress?
Yes, within reasonable limits such as 300 seconds.
Why does this happen during imports or updates?
These tasks process large amounts of data and may exceed default execution time.
Can this error occur even on fast hosting?
Yes. All servers enforce execution time limits to prevent runaway scripts.
Does this error delete site data?
No. The process stops, but existing data remains intact.
Written by TechHelpTips Editorial Team
We publish clear, step-by-step guides for common website and WordPress issues, focusing on safe, non-destructive fixes that help restore normal site functionality without unnecessary changes.
